Introduction:
Protein is a vital macronutrient that plays a crucial role in the overall functioning of our bodies. It is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and regulating various physiological processes. Inadequate protein intake can lead to a condition known as protein deficiency, which can have a significant impact on our health and well-being. This comprehensive guide aims to help you identify protein deficiency symptoms and understand the importance of maintaining an adequate protein intake in your diet.
The Importance of Protein

Protein is often referred to as the building block of life. It is composed of amino acids, which are the structural units necessary for various bodily functions. There are 20 different amino acids, and our bodies require all of them to function optimally. Of these, nine are considered essential amino acids, meaning that our bodies cannot produce them and must obtain them from our diet. The remaining 11 are non-essential amino acids, which our bodies can synthesize.
Protein plays a wide range of critical roles in the body, including:
Muscle Growth and Repair: Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissues. This is particularly important for athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals recovering from injuries.
Immune Function: Many immune system components, including antibodies, are made of protein. A deficiency can weaken the immune system’s ability to fend off infections and illnesses.
Hormone Production: Some hormones, like insulin and growth hormones, are protein-based. These hormones regulate various physiological processes in the body.
Enzyme Activity: Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in the body, facilitating digestion, metabolism, and other vital processes.
Transport and Storage: Proteins play a role in transporting substances like oxygen (hemoglobin) and fat (lipoproteins) in the bloodstream.
Identifying Protein Deficiency Symptoms
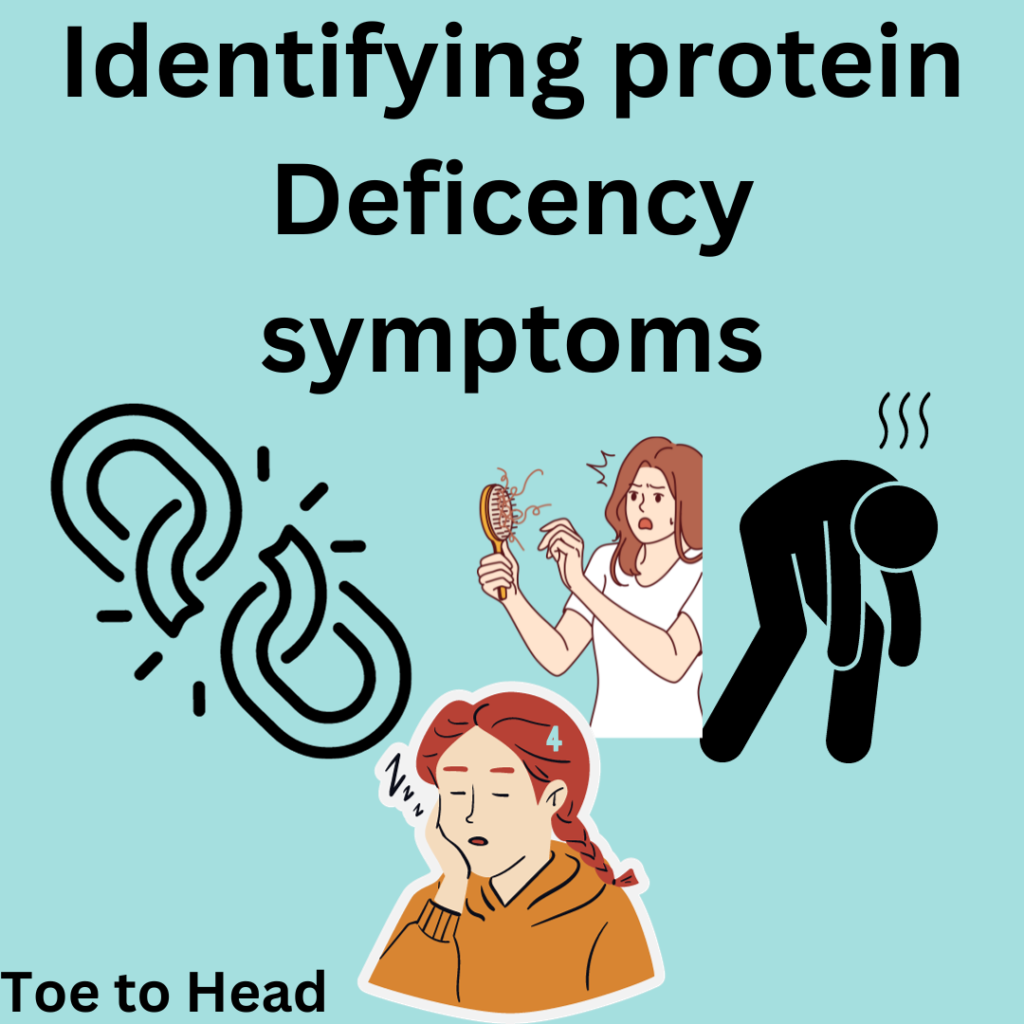
- Muscle Weakness and Atrophy: Inadequate protein intake can result in muscle weakness and even muscle atrophy over time. Individuals who don’t consume enough protein may find it challenging to build and maintain lean muscle mass.
- Edema (Swelling): Protein helps maintain the balance of fluids in the body. A lack of protein can lead to edema, which is the accumulation of excess fluid, causing swelling, especially in the hands, feet, and ankles.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Insufficient protein can lead to feelings of fatigue and weakness. This is because proteins are a source of energy and play a crucial role in the production of enzymes and hormones that maintain energy levels.
- Hair, Skin, and Nail Problems: Protein deficiency can result in brittle hair, dry and flaky skin, and weak, easily damaged nails. These symptoms may be particularly noticeable if the deficiency persists.
- Poor Wound Healing: Protein is essential for tissue repair and wound healing. A lack of protein can lead to delayed wound healing and an increased risk of infection.
- Mood Changes: Amino acids are the precursors to neurotransmitters, which regulate mood and mental health. A deficiency in essential amino acids can lead to mood swings, irritability, and even depression.
- Increased Susceptibility to Infections: A weakened immune system due to a lack of protein can make individuals more vulnerable to infections and illnesses.
- Changes in Hair Color: In severe cases of protein deficiency, hair color may change, becoming lighter or losing its pigmentation.
- Fragile Bones: Proteins are essential for bone health, and a deficiency can lead to weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: Protein deficiency can result in digestive issues such as diarrhea and abdominal pain.
Preventing Protein Deficiency

Preventing protein deficiency is crucial for maintaining good health. To ensure you are getting an adequate amount of protein in your diet, consider the following:
- Diverse Diet: Consume a variety of protein sources, including lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This will help you obtain a wide range of amino acids.
- Protein Supplements: If you have dietary restrictions, allergies, or find it challenging to meet your protein needs through food alone, protein supplements like protein powders or shakes can be a convenient option.
- Balanced Meals: Include protein-rich foods in every meal. This will help ensure a steady supply of amino acids throughout the day.
- Consult a Dietitian: If you’re unsure about your protein intake or have specific dietary requirements, consult a registered dietitian who can help you create a balanced diet plan.
Conclusion:
Protein is a fundamental nutrient that supports a wide range of critical functions in the body. Protein deficiency can lead to a variety of symptoms and health issues, including muscle weakness, edema, fatigue, and more. To prevent protein deficiency, it’s essential to maintain a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of protein sources. If you suspect you may be deficient in protein or have concerns about your dietary choices, consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure you’re meeting your protein needs for optimal health and well-being. Remember, identifying and addressing protein deficiency early can help you lead a healthier, more vibrant life.