Introduction:
Peanut butter is a beloved and versatile spread that many people enjoy as a part of their daily diet. It’s packed with protein, healthy fats, and a wide range of essential nutrients, making it a popular choice for sandwiches, smoothies, and more. However, when it comes to health-conscious food choices, questions often arise, such as whether peanut butter contains trans fat. In this article, we’ll explore the truth about trans fats in peanut butter and how it may impact your health.
Understanding Trans Fats
Trans fats, short for trans-unsaturated fatty acids, are a type of unsaturated fat with a unique chemical structure. Unlike healthy unsaturated fats, which are typically found in foods like avocados and nuts, trans fats are artificially created through a process called hydrogenation. This process involves adding hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them solid at room temperature. Trans fats are often used in processed and fried foods to extend shelf life and improve texture.
Trans fats have been extensively studied, and their consumption has been linked to several health issues, including an increased risk of heart disease, high cholesterol levels, and inflammation. As a result, many health experts advise limiting trans fat intake.
Peanut Butter and Trans Fat
The good news for peanut butter lovers is that most natural, unprocessed peanut butter does not contain trans fats. Natural peanut butter typically consists of just two ingredients: peanuts and sometimes a pinch of salt. Since it is not hydrogenated, it remains free from trans fats. However, it’s essential to carefully check the product label to ensure that you are indeed purchasing natural peanut butter, as some commercial varieties may contain hydrogenated oils or partially hydrogenated oils, which can introduce trans fats into the mix.
Reading Labels
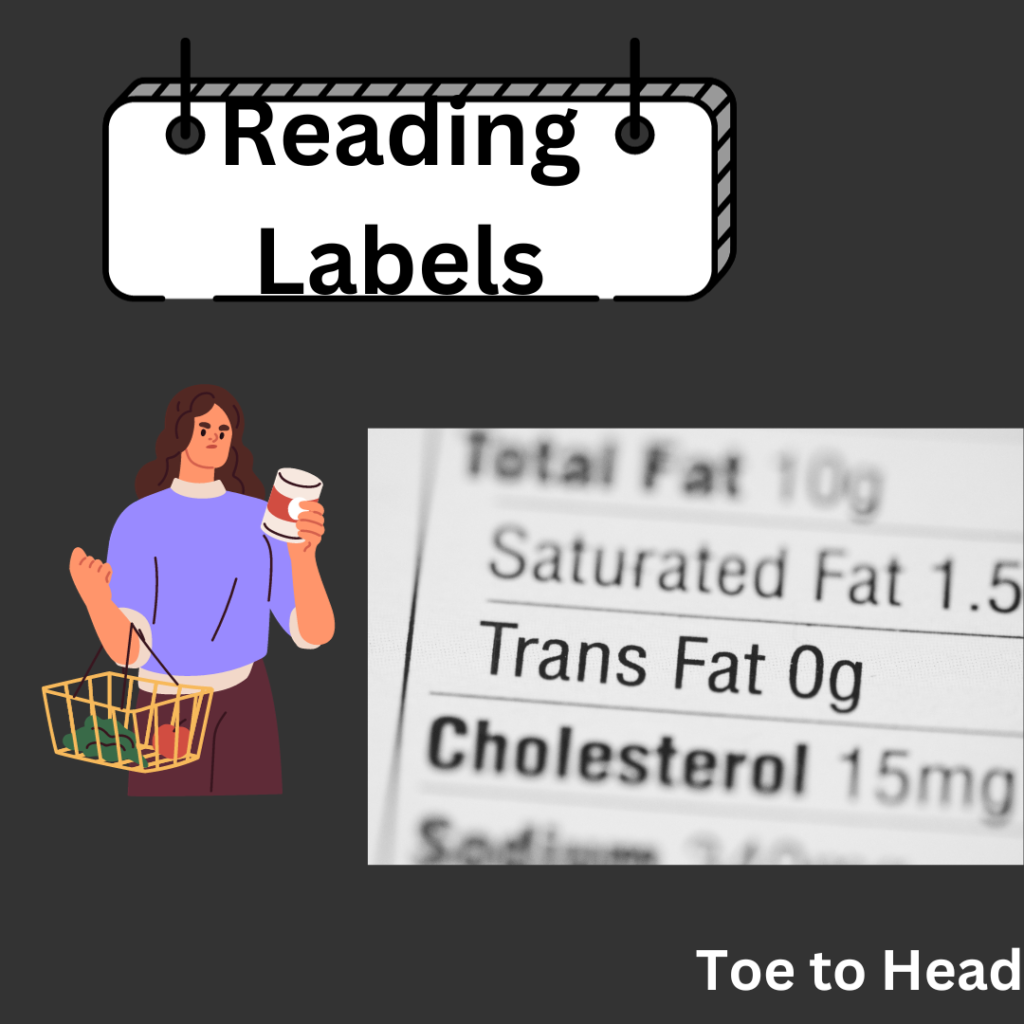
To determine whether the peanut butter you’re considering contains trans fat, it’s crucial to examine the product’s nutritional label. Here are a few tips on what to look for:
Ingredient List: Natural peanut butter should contain only two ingredients: peanuts and possibly salt. If you see the words “partially hydrogenated” or “hydrogenated” in the ingredient list, it indicates the presence of trans fats.
Trans Fat Content: In the nutrition facts panel, check for the “Trans Fat” line. If it reads “0 grams,” it means the product contains negligible amounts of trans fat, which is generally considered safe. However, be cautious if it states any amount greater than zero.
Responses to some of the questions you have in your mind:
Do all peanut butters have trans fat?
No, not all peanut butters contain trans fat. In fact, most natural peanut butters, which are made with just peanuts (and possibly a bit of salt), do not contain trans fats. It’s important to check the product label and ingredient list to ensure you are choosing a trans fat-free option. Avoid peanut butters that include hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils in their ingredients, as these can introduce trans fats.
Is peanut butter a bad fat?
Peanut butter, particularly natural peanut butter, is not considered a “bad” fat. It primarily contains healthy unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can have several health benefits. These fats are known to reduce LDL cholesterol levels and lower the risk of heart disease. However, like all foods, moderation is key, as peanut butter is calorie-dense. Enjoy it as part of a balanced diet for its numerous nutritional benefits.
What foods are high in trans fat?
Foods that are high in trans fat typically include processed and fried foods. These can range from commercially baked goods like cookies, cakes, and pastries to certain margarines, microwave popcorn, and deep-fried fast foods. Trans fats are often found in foods made with partially hydrogenated oils. To make healthier choices, it’s best to avoid or limit consumption of such processed and fried items.
Is peanut oil a trans fat?
Peanut oil, when in its natural form, does not contain trans fat. It is primarily composed of unsaturated fats, similar to the fats found in peanuts themselves. However, if peanut oil has been subjected to the hydrogenation process to make it solid at room temperature (partially hydrogenated peanut oil), it can contain trans fats. So, the presence of trans fat in peanut oil depends on whether it has undergone hydrogenation. Natural, unhydrogenated peanut oil is trans fat-free.
Benefits of Natural Peanut Butter

Opting for natural peanut butter offers several health benefits beyond being trans fat-free. It’s rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help improve heart health by reducing LDL cholesterol levels and decreasing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, natural peanut butter provides essential nutrients like protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
While it’s calorie-dense, the combination of healthy fats and protein in natural peanut butter can help you feel full and satisfied, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Moreover, the presence of antioxidants, such as resveratrol, can contribute to its anti-inflammatory and potential cancer-fighting properties.
Conclusion
In summary, most natural peanut butter does not contain trans fats, making it a healthy and delicious choice for individuals looking to incorporate nutritious fats into their diets. However, it’s essential to read product labels carefully and choose peanut butter made solely from peanuts and perhaps a pinch of salt. Natural peanut butter can be a valuable part of a well-balanced diet, offering a wealth of nutrients and potential health benefits. By making informed choices, you can continue to enjoy this beloved spread while supporting your overall health and well-being.